Arteries and Veins both are blood vessels of the vascular system of the human body and play a role in the transportation of blood throughout the body. Arteries are the thick-walled muscular tubes that carry oxygenated blood towards the body organs and tissues for nutrition. On the contrary, Veins are thin-walled blood tubes that carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart for oxygenation. Both arteries and veins are components of the vascular system of Veins the human body and play a vital role in the transportation of blood throughout the body for the nutrition of the tissues and the organs.
Contents
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Arteries | Veins |
| Definition | Blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood from the heat to the tissues of the body are called arteries. | Blood vessels that carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues of the body to the back of the heart are called veins. |
| Color | Red in color because of oxygenated blood | Blue in color because of deoxygenated blood |
| Location | Deep in the body organs | Present near the surface of the skin or deeper in the skin. |
| Lumen | Narrow lumen | Wide lumen |
| Thickness of walls | Thick-walled with more elasticity | Thin-walled with less elasticity |
| Layers | Three layers | Three layers |
| Types | Pulmonary and systemic arteries | Superficial veins, deep veins, pulmonary veins, and systemic veins |
| Blood pressure | High | Low |
| Blood volume | Almost 30% | Almost 65% |
| Pulse | Detectable in the arteries | Detectable in the veins |
| Valves | No valves | Valves present |
| Disease | Atherosclerosis | Deep vein thrombosis |
What is Arteries?
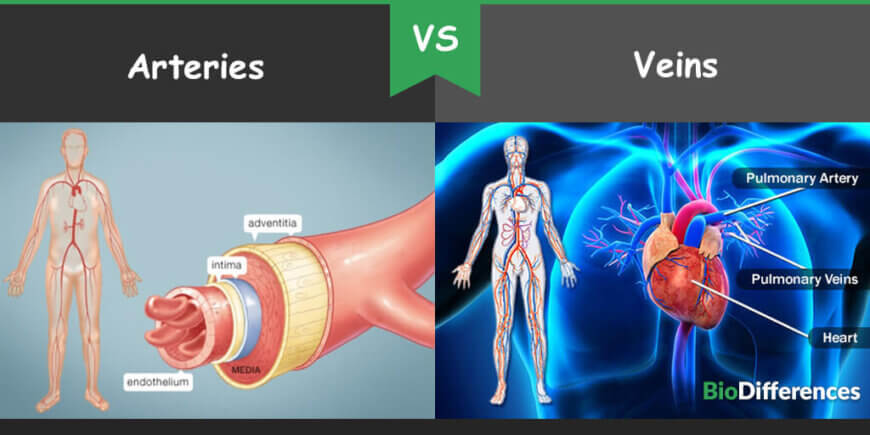
The word “arteries” is the plural form of the artery. It is the blood vessel that delivers oxygenated blood with other nutrients from the heart to all tissues of the body. It has been studied in the human physiology. Arteries are the muscular tubes in soft tissues and have three layers; the intima, the media, and the adventitia. During the pumping action of the heart, these muscular tubes transport blood under the high pressure towards all the body.
Intima is also called tunica intima, which is the inner layer of the wall of an artery. It has direct contact with the flowing blood. The media, also known as Tunica Media, is the middle layer. It is composed of elastic fibers and smooth muscles. The adventitia, also known as Tunica Adventitia, is the outermost layer of the artery. It is composed of elastic fibers, collagen, and the connective tissues.
The largest artery of the heart, aorta, arises from the left ventricle of the heart. Its structure has many small branches known as smaller arteries. These small arteries are divided into the sub-branches called arterioles. Further sub-branches of the arterioles are known as capillaries. The arteries and their sub-branches arterioles have more smooth muscles to regulate the changing pressure during blood flow. This pressure is the result of the pumping of the heart. It is of two types; the diastolic pressure and systolic pressure. In the diastolic phase, the heart is considered in the rest position. In this phase, blood pressure is low. In the systolic phase, blood pressure is high because of the contraction of muscles of the heart. This pressure forces the blood into the arteries. This change in pressure is felt at the time of checking the pulse rate. All arteries carry oxygenated blood except the pulmonary artery, which carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs. Lungs remove carbon dioxide from the blood.
What is Veins?
Veins are also components of the vascular system and perform functions just opposite to the arteries. When blood is used by all the tissues to get oxygen and other nutrients, and all waste materials and carbon dioxide are given to the blood from the tissues and organs, it is returned back to the heart through veins. The blood saturated with carbon dioxide and waste materials are called deoxygenated blood. When this deoxygenated blood is carried to the heart, the heart sent it to the lungs, which carbon dioxide is replaced with the oxygen and is again sent to the tissues and organs of all body to get nutrients.
Veins are of different sized depending on the location and function. The largest vein is located in the center of the body and connected with the all small veins of the body. It collects all the deoxygenated blood by all small veins so it is the collection center. The superficial veins are the veins closer to the skin whereas deeper veins are located in the center of the body. The superficial veins and deep veins are connected with each other through perforating veins.
Veins also have three layers; Tunica intima, Tunica media, and Tunica adventitia. The tunica intima is the inner layer composed of soft tissues and muscles and has direct contact with flowing blood. The tunica media is the middle layer and is composed of elastic fiber and smooth muscles. The third layer, stronger outer covering, Tunica adventitia is composed of collagen, elastic fibers, and connective tissues.
All veins carry deoxygenated blood towards the heart except the pulmonary vein. It carries oxygenated blood back to the heart from the lungs.
Key Differences between Arteries and Veins
- Arteries carry blood away from the heart to tissues except for pulmonary arteries whereas veins carry blood towards the heart from tissues except for pulmonary veins.
- Arteries are composed of thick elastic muscular walls whereas veins are composed of thin nonelastic muscular walls.
- In arteries, blood passes through high blood pressure whereas, in veins, blood passes through low blood pressure.
- In arteries, valves are absent whereas in veins valves are present to prevent backflow of blood.
- Arteries are usually positioned deeper in the skin whereas veins are positioned near the surface of the skin, sometimes also deeper.
- Arteries will remain open if the blood flow stopped because of elastic nature whereas veins will collapse if the blood flow is stopped.
- Two main diseases that affect the arteries are atherosclerosis and myocardial ischemia whereas deep vein thrombosis affects the veins.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both arteries and veins are the main components of the blood circulation system of the body and play a significant role in blood flow. But both differ from each other in various aspects.