Cysts and tumors are two common types of medical conditions and physically appear in the form of lumps. They can be present in the same place, so it isn’t very easy to differentiate between them. Sometimes, it is also possible to have both ovarian cyst and ovarian tumors. However, both are usually different medical conditions with different characteristics.
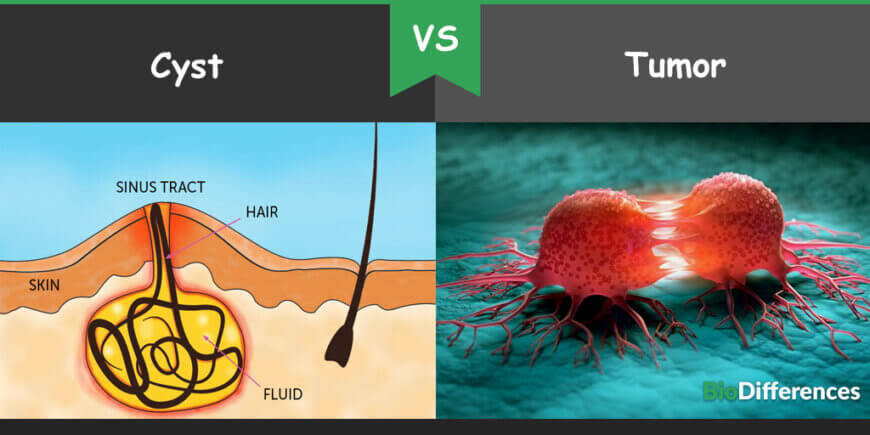
Cysts are sacs filled with air, fluid, or sometimes with other materials. These are soft physically. They can appear anywhere in the body; soft tissues, organs, or bones. There are different causes of cysts such as infections, chronic inflammatory conditions, and excessive production from sebaceous glands and obstruction to the flow of fluids or foreign particles. These cysts are usually discovered during the physical examination, but some require ultrasound imaging for diagnosis.
The word “tumor” and “cancer” are usually used interchangeably, but both can differ in many aspects. Tumors are commonly known as neoplasms. These are abnormal tissue masses that can grow on almost any body part. Tumor tissues become faster than healthy tissues. All tumors are not lethal; some are benign. Benign tumors are harmless unless interfering with normal body functions.
Contents
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Cyst | Tumor |
| Definition | The cyst can be defined as a pouch or a sac-like outgrowth present in any part of the body filled with air, fluid, or other material. | The tumor can be defined as the uncontrolled cell division and growth of the cells in any area of the body. |
| Causes | Different medical conditions, genetic causes, injuries, infections, ovulation, degeneration of the tissues | Abnormal cell growth, formation, and multiplication of the cells, the survival of the old and damaged cell |
| Types | Breast cysts, Epidermoid cyst, hepatic cyst, pilar cyst, renal cyst, ovarian cyst. | Benign tumor and malignant tumor |
| Diagnosis | Physical examination, by diagnostic imaging, and by fine needle aspirations. | By physical examination and biopsy. |
| Treatment | Usually drainage of fluid from the cyst | Chemotherapy and radiotherapy |
What is Cyst?
A cyst is a small lump or sac of tissues filled with air, liquid, or semi-solid material. It can seem on any area of the body. Most of the cysts are non-cancerous and harmless. Its treatment depends on different factors such as type of the cyst, location of the cyst, or whether the cyst is infected or not. The cyst can appear in people of any group, age, or area. There are almost a hundred types of cysts and may occur due to different medical issues. Ovarian cysts, sebaceous cysts, breast cysts, chalazia cysts, pilonidal cysts, ganglion cysts, epidermoid cysts, bakers cysts, dermoid cysts, nabothian cysts and cystic acne are some examples of commonly occurring cysts. Cysts can be caused by various reasons. Wear and tear or small defects during embryonic development and small blockage in the flow of body fluid are some reasons for cysts. Chronic inflammation inherited the disease, infections and tumors are a risk factor of cysts.
Types
Cysts can be small or large. The types of cysts depend on the area or organ in which they are found, such as pancreatic cyst, vaginal cyst, breast cyst, kidney cyst, a skin cyst, thyroid cyst and liver cyst.
Diagnosis
Cysts can be diagnosed by physical examination through the naked eye. However, in some cases, cysts require diagnostic imaging. These images help doctors to figure out what is inside the lump. These diagnostic images are CT scans, ultrasound, MRI scan and mammograms. Benign cysts appear smooth both through naked eyes and diagnostic images. Cysts containing solid compound due to tissue rather than air or liquid can be either benign or malignant. Cysts can be treated by the general physicians or surgeon and depend on their size.
What is Tumor?
The tumor is an abnormal growth of the mass of tissue due to the continuous division and growth of the cell. The cell growth in the tumor is rapid and in an uncontrolled way, which gives rise to accumulation of the abundance of cells in an area and develops an enlarged morbid or swelling. Neoplasm is the synonym of the tumor but not of cancer. Some tumors can be cancerous due to the potential of the cell present in it, which can metastasize and spread from one area to another area. Tumors can be of two types; benign (non-cancerous) and malignant (cancerous).
Types
There are two types of tumors; benign tumor and malignant tumor.
Benign Tumor: It is a harmless tumor and does not cause cancer. In this type of tumor, cells do not spread or invade nearby tissues. Although benign tumors can be harmful if they affect the blood vessels and nerves, the reason for benign tumors can be a long term infection, stress, diet, or exposure to radiation. These tumors do not need any treatment until they are not harmful to the other nearby tissues. Standard therapy for benign tumors is surgery. Fibromas, Lipomas, Myomas, Papillomas, Adenomas and Osteochondromas are few types of benign tumors.
Malignant Tumor: Malignant tumor is the cause of cancer and can be proved very lethal. These tumors are very resistant to any treatment and have the potential of spreading to any other part of the body. These tumors also can reoccur. Cells of malignant tumors show uncontrolled and abnormal division. The diagnosis and treatment are based on the location of the tumor in the body. Tumor markers and other imaging techniques are used to diagnose malignant tumors. Malignant tumors are treated through chemotherapy, surgery and radiotherapy. Carcinoma, Sarcoma, Germ cell tumor and Blastoma are some examples of the malignant tumors.
Key Differences
- A cyst is a sac filled with air or fluid, whereas the tumor is a solid mass of tissues.
- A cyst is caused by an infection or obstruction of a gland, whereas a tumor is caused by a genetic cause.
- A cyst is usually soft because of content, whereas the tumor is solid because of tissues or cells.
- Most cysts are benign, whereas tumors can be benign or malignant.
- Cysts can result in different complications, whereas tumors are life-threatening on becoming malignant.
Key similarities
- Both cyst and tumor can appear in tissues, organs, or bones.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both cysts and tumors are medical conditions that can be either harmless or harmful. Both are lumps in the skin but differ from each other in many aspects.