The immune system of the human body is a very effective defense mechanism against viral, bacterial and other infections. It recognizes the foreign particles and protects the human body by eliminating these foreign particles. The immune system is a complex system consisting of many cells and tissues. It is essential for human survival.
Foreign particles that attack the body are termed an antigen. Bacteria and viruses are also called antigens in referring to the immune system. The immune system produces an antibody against every antigen. An antibody can be a carbohydrate or a protein that evokes immune response resulting in the development of antibodies. Antibodies are also called immunoglobulin. Ig stands for immunoglobulin. Antibody or immunoglobulin is proteinaceous and binds to the antigens in specific cases. Antibodies are produced by the B-lymphocytes, which are the types of white blood cells. There are five types of antibodies; IgM, IgG, IgD, IgA, and IgE.
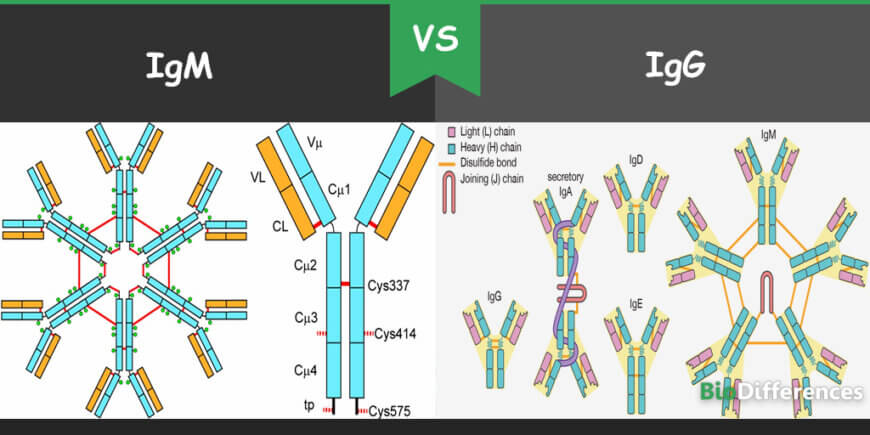
Both IgM and IgG are also classes of immunoglobulin or antibodies. IgM is the first ever antibody to be produced against any foreign particle invasion, whereas IgG is the most abundantly found antibody in the body. IgM is the largest antibody among all with pentamer units and ten binding sites for antigens. IgG is responsible for humoral immunity and is a monomer lighter and smaller unit with two binding sites for antigens. Its smaller size enables it to travel through the bloodstream. Besides these, there are many other differences between these two immunoglobulins.
Contents
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | IgM | IgG |
| Molecular weight | 900 kDa | 150 kDa |
| Presence in serum | 10% of the total weight | 75% of the total weight |
| Percentage in carbohydrates | 12% | 3% |
| Heavy chain | Mu (µ) | Gamma (γ) |
| Light chain | Kappa (κ) and lambda (λ) | Kappa (κ) and lambda (λ) |
| Types | No types | Four types:
IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, and IgG4 |
| Size | Larger | Smaller |
| Location in body | Lymph fluid and blood | Lymph, blood, and intestine |
| High levels effects | Parasitic infections, kidney damage, rheumatoid arthritis, hepatitis and mononucleosis | HIV, multiple sclerosis, multiple myeloma |
| Low levels effects | Leukemia, some inherited diseases | Kidney damage and few types of infections |
| Function | It provides the first kind of and immediate defense response. | Provides long term defense response against infections |
What is IgM?
All antibodies are proteins produced by B-lymphocytes. B-lymphocytes are types of white blood cells. IgM is the largest antibody present in blood and lymph and produced by the plasma cells. IgM is the first antibody developed in response to any foreign particle or antigen and very useful in evading any bacteria, viruses and other pathogens. The quantity of IgM produced at the time of initial exposure to antigen is six times greater than IgG. It is the largest immunoglobulin with five Y shaped units (pentamer) bounded with a polypeptide bond. Because of its larger size, IgM is unable to cross the placenta even though it is the first antibody produced in the fetus.
IgM has ten antigen-binding sites with the heavy chain mu (µ) and light chain unit of kappa (κ) and lambda (λ). However, only five sites are functional antigen-binding sites. As the size of IgM is more significant as compared to other antibodies; hence their presence is only 10% of the total blood serum.
Despite the primary defense response, IgM gives a transient response and disappear within two or three weeks after their production. High levels of IgM may give rise to parasitic infections, rheumatoid arthritis, kidney damage, hepatitis and mononucleosis. Even if the quantity of IgM is high in the newborn, it means the child had already contracted an infection in the mother’s womb before birth. Low level of antibody IgM results in few types of myeloma, leukemia and some inherited diseases. So we may say that the presence of IgM marks certain kinds of infection in the body.
What is IgG?
IgG accounts for almost 75% of the total weight of the blood serum. It is the most abundant immunoglobulin in the body produced by white blood cells. IgG is the smallest antibody among all antibodies consisting of only a single Y shaped monomer. It has two binding sites for antigens with heavy chains of gamma and light chain of kappa and lambda.
IgG provides a long term response to any infection or disease. It has four further types; IgG1, IgG2, IgG3 and IgG4. Because of small size, it travels through the bloodstream and it is the only antibody that can cross the placenta and transfer mother’s immunity to the developing embryo. It is produced at the later stages of infection but provides a long time effect for the complete eradication of infectious diseases. For instance, if a child is exposed to chickenpox, he will show high levels of IgM in the blood in the period following the exposure. Once the kid gets the disease, he shows long term immunity against the disease by developing IgG antibodies.
IgG plays a vital role in the production of the secondary immune response against any antigen causing opsonization, phagocytosis and in fighting with viruses and bacteria. A high quantity of IgG in the body means a long term infection like multiple sclerosis, HIV, and multiple myeloma. The low amount of IgG results in kidney damage and other diseases.
Key Differences
- IgM composes about 10% of the total volume of the serum, whereas IgG composes about 75%of the total serum.
- IgM has a molecular weight of about 900 000 MW, whereas IgG has a molecular weight of about 150,000 WM.
- IgM provides a dense primary response, whereas IgG provides a secondary defense response.
- IgM has no further subtype, whereas IgM has four types; IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, and IgG4.
- IgM provides a temporary defense mechanism, whereas IgG provides long term defense mechanism.
- IgM has a heavy chain in the unit if mu (µ), whereas IgG has a heavy chain in the unit of gamma (γ).
- IgM is found in the plasma cells, blood, and lymph fluid, whereas IgG is found in lymph, blood, and intestine.
- The presence of IgM shows the current infection, whereas the presence of IgG shows the past disease.
- IgM is larger, so it cannot cross the placenta, whereas IgG is smaller in format and crosses the placenta.
- IgM is a pentamer unit with 10 antigen-binding sites, whereas IgG is a monomer with two antigen-binding sites.
Key Similarities
- Both IgM and IgG play a role in the defense mechanism.
- Both IgM and IgG have light chains in the unit of kappa (κ) and lambda (λ).
Conclusion
In conclusion, both IgM and IgG are types of antibodies produced by the immune system of humans for identification, neutralization, and destruction of antigens (disease-causing foreign particles) with many differences.