The plant’s body is also composed of cells and tissues. Xylem and phloem are complicated vascular tissues of the plants and acts as a unit and perform transportation of food and water in the plants. Xylem and phloem constitute vascular bundles together and provide food, water, and other minerals towards all parts of the plants such as stems, roots, and leaves of the plants.
Although both types of tissues perform the same function but have many differences.
Contents
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Xylem | Phloem |
| Definition | Xylem is dead, complicated and permanent vascular tissue of plants responsible for transportation. | Phloem is living and permanent vascular tissue of plants responsible for the transportation of food in the plant. |
| Etymology | The Greek word which means wood | The Greek word which means bark |
| Type of cells | Dead cells except for parenchyma | Living cells except for fibers |
| Comprise of | Xylem bundles, fibers and tracheids | Phloem fibers, sieve tubes, sieve cells, phloem parenchyma and companion cells |
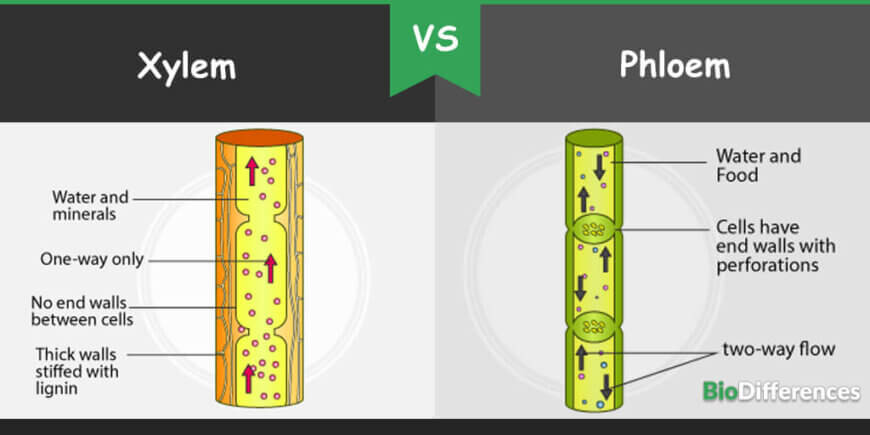
| Structure | Tubular shape with no cross walls | Elongated, tubular shape with thin-walled sieve tubes |
| Shape | Star-shaped | Not of star-shaped |
| Location | present in the middle of the vascular bundle, deep in the plants. | Present on the outer side of the vascular bundle. |
| Type of flow | Unidirectional (upward flow) | Bi-directional (upward and downward flow) |
| Function | Transportation of water, mineral and food through the roots to provide mechanical support. | Transportation of water, mineral and food towards the green parts. |
What is Xylem?
The term “xylem” was introduced by Carl Nageli in 1858. It has derived from the Greek language and it means wood. Xylem is dead, complicated and permanent vascular tissue. Xylem is composed of vessels and tracheary elements like tracheids vessels, xylem parenchyma. These are thickly walled located in the center of the cell.
Xylem is of two kinds; primary xylem and secondary xylem depending on the pattern of lignin. Primary xylem is originated during primary growth from procambium. It has protoxylem and metaxylem. Metaxylem develops after the protoxylem but before secondary xylem. Metaxylem has more full vessels and tracheids than protoxylem. Secondary xylem is evolved during secondary growth from vascular cambium. Secondary xylem is found in two main groups of plants; conifers and angiosperms.
In xylem vessels, water travels by bulk flow rather than cell diffusion. Negative pressure facilitates the movement of water and minerals. Soluble mineral nutrients and water is taken from the roots to the various parts of the plant. The primary function of the xylem is to transport water and nutrients to all regions, but it is also involved in replacing water lost through transpiration and photosynthesis. Xylem also offers mechanical support to the plant.
What is Phloem?
Phloem is also the other type of vascular tissue introduced by Carl Nageli in 1858. Phloem is of Greek language word which means bark. Phloem surrounds the xylem. These are living and permanent vascular tissues responsible for the transport of food and other organic nutrients in the plant. These organic nutrients are called photosynthates, which is glucose.
In phloem, the concentration of organic substances inside a phloem cell creates a diffusion gradient by which water flows into the cells, and phloem sap moves from source or organic substance to sugar sinks by turgor pressure. In phloem, positive hydrostatic pressures are responsible for transportation. Phloem loading and unloading bring about translocation. It translocates sugar made by photosynthetic areas of plants to storage organs like tubers, roots, or bulbs.
Key Differences
- Xylem is the complex vascular tissue of the plants responsible for the transportation of the food and water towards all parts of the plant. In contrast, the phloem is another living vascular tissue responsible for the transportation of the food and water towards the green parts of the plant, such as leaves.
- The word “xylem” has derived from the word “xylon” means wood, whereas the word “phloem” has derived from “pholos” means “bark.”
- In xylem, the flow of food towards the parts is unidirectional, from the root to the upper part of the plant, whereas the flow of material in the phloem is bidirectional.
- Xylem is composed of dead cells and only living parenchyma cells, whereas the phloem is composed of living cells and only dead fibers.
- Xylem is present in the center of the vascular bundles, deep in the plant and made up of xylem vessels, fiber and tracheids whereas phloem is located on the outer side of the vascular bundles and made up of phloem fibers, sieve tubes, sieve cells, phloem parenchyma and companion cells.
- Xylem fibers are small whereas phloem fivers are large.
- In mature plants, xylem has differentiated into heartwood and sapwood whereas no such differentiation occurs in the phloem.
- Xylem lives with the hollow dead cells, whereas phloem lives with the cytoplasm without the nucleus.
- Xylem also provides mechanical strength to the plant, whereas the phloem is not capable of giving mechanical support to the plant.
- Xylem often contains the bulk of the plant body, but the conducting cells are dead, whereas phloem formulae a small part of the plant body and the conducting cells are living.
Key Similarities
- Both xylem and phloem are present in the cellulose of the cell wall.
- Both are present in primary and secondary vascular tissues.
- Both xylem and phloem have chloroplast in the structure.
- Both have vascular tissues which help in the transportation of material throughout the plant.
- Both have parenchymatous cells.
- Both play an essential role in primary and secondary growth.
- Both are introduced by Carl Nageli in 1858 for the first time.
Conclusion
In conclusion, xylem and phloem are vascular tissues of the plants with some structural differences, but the function of both is the same, transportation of food.