Fertilization is the mechanism of sexual reproduction which forms the zygote. The zygote is developed into a new organism. In fertilization, the union of sperm (male gamete) with the egg (female gamete) occurs to produce diploid cells or zygote. Fertilization is of two types; internal fertilization and external fertilization. Both occur in various groups of animals.
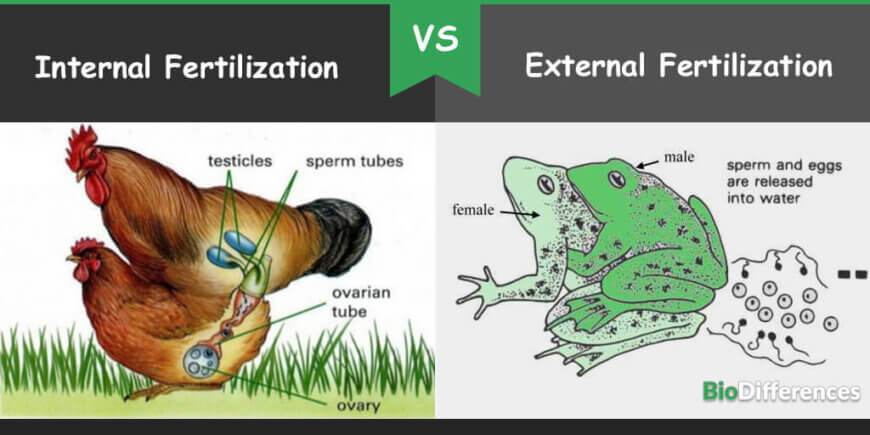
Internal fertilization is the process of union of male and female gametes inside the female body after insemination using copulation whereas external fertilization is the union of male gamete with female gamete outside the body, usually in the outer environment, especially in water bodies.
Internal fertilization occurs in the mammals and birds whereas external fertilization is followed by mostly aquatic animals and a few amphibians.
Contents
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Internal Fertilization | External Fertilization |
| Definition | The process of syngamy inside the female body is called internal fertilization | The process of syngamy outside the female body, in the outer environment is called external fertilization |
| Number of gametes released | Less number of gametes | Numerous gametes are released |
| Syngamy | Occurs inside the body | Occurs outside the body |
| Survival rate | High survival rate | Low survival rate |
| Environmental conditions | In harsh environment | In moistened environment |
| Genetic diversity | No great genetic diversity | Greater genetic diversity |
| Types | Three types: oviparity, Viviparity and ovoviviparity | No further types |
| Example | Birds, reptiles, mammals, Bryophytes and tracheophytes | Algae, fish and amphibians |
What is Internal Fertilization?
Internal fertilization occurs in plants as well as in terrestrial animals and in a few aquatic animals. In plants, this type of fertilization occurs inside the ovary in some higher plants, such as angiosperms, pteridophytes, gymnosperms and bryophytes but not in non-vascular plants. This type of fertilization occurs in three ways; oviparity, viviparity and ovoviviparity.
Oviparity fertilization occurs in animals that lay eggs outside and the nourishment is provided to the offspring by the presence of the yolk in the egg. The animals in which oviparity occurs are called oviparous such as birds, amphibians, reptiles, bony fish and a few cartilaginous fish.
Viviparity method is followed by a few reptiles, mammals and cartilaginous fish. In this fertilization, the offspring develop within the body of a female and receive nourishment through the placenta from the mother’s blood. After the development, the offspring comes out of the mother’s body. These animals are known as viviparous.
In ovoviviparity, the eggs are kept in the female body and the nourishment is provided from the yolk present in the egg only to the developing embryo. When the young one is fully developed, the egg is hatched and the young one comes out. Lizards, snake ad sharks follow this type of internal fertilization.
Advantages
In internal fertilization, as the fertilized egg remains inside the body of a female, so is protected from the predators as well as from the harsh climate. Hence, the chances of survival of the offspring are higher.
In internal fertilization, the mates are selective and there are lesser chances of desiccation of gametes.
Disadvantages
There are a few disadvantages of internal fertilization. Firstly, there is a lesser number of offspring produced at a given time. Sometimes, it is difficult for the male and female to come into intimate contact. For the internal fertilization, male must produce a large number of sperms. But only one sperm fertilizes one egg at a time. Internal fertilization also requires close coordination between males and females in terms of behavior and physiology which needs extensive hormonal control. In this fertilization, females contribute more than males.
What is External Fertilization?
External fertilization is a mode of reproduction in which a male organism’s sperm fertilizes a female organism’s egg outside of the female’s body. This type of fertilization happens in water or a moist area to facilitate the movement of the sperm to the egg.
Fish, sea urchins, a few vertebrates, all aquatic invertebrates and most amphibians show external fertilization in which male and female sex cells unite in the external environment. Sperms and eggs are deposited into the open surrounding which is called spawning. In another method, the sperms swim through the water to get unite with the eggs and get fertilized which is called broadcast fertilization.
Advantages
There are several advantages of the external fertilization. Firstly, the offspring produced by this fertilization are higher in number and there is less competition between offspring and their parents. Secondly, less energy is required to find a mate contrary to internal fertilization. External fertilization results in a greater genetic variation among offspring.
Disadvantages
There are also some disadvantages of external fertilization. There are a few chances of survival of the offspring as the parents can not provide care to each offspring. A large number of unfertilized gametes will be wasted due to unprotection as well as from desiccation. Secondly, male parent must produce a large number of sperms as each sperm may not fertilize the egg. Similarly, females must deposit dozens of eggs for successful fertilization. Predators and other environmental hazards minimize the probability of external fertilization.
Key Differences
- Internal fertilization is the process of fusion of sperm with an egg inside the female body whereas external fertilization is the process of fusion of sperm with the egg outside the body.
- In internal fertilization, a smaller number of gametes are released whereas in external fertilization, numerous gametes are released into the environment.
- Internal fertilization shows high survival rates of the embryo whereas external fertilization shows lower survival rates of the embryo and egg.
- In internal fertilization, a smaller number of gametes are produced whereas in external fertilization, a large number of gametes are produced.
- Offspring of the internal fertilization is very successful in harsh environmental conditions whereas offspring of the external fertilization is successful in moistened environments.
- Internal fertilization shows no greater genetic diversity whereas external fertilization results in great genetic diversity.
Key Similarities
- Both internal fertilization and external fertilization occurs in plants and animals.
- The final product in both internal and external fertilization is the zygote.
- Both involve fusing of the male gamete with the female gamete.
- Mobile male gamete and immobile female gametes are produced in both types of fertilization.
Conclusion
In conclusion, internal and outer fertilization are two types of fertilization which differ in one aspect which is that in internal fertilization, syngamy occurs inside the female body whereas in external fertilization, syngamy occurs outside the female body. Both types of fertilizations have some advantages as well as disadvantages.