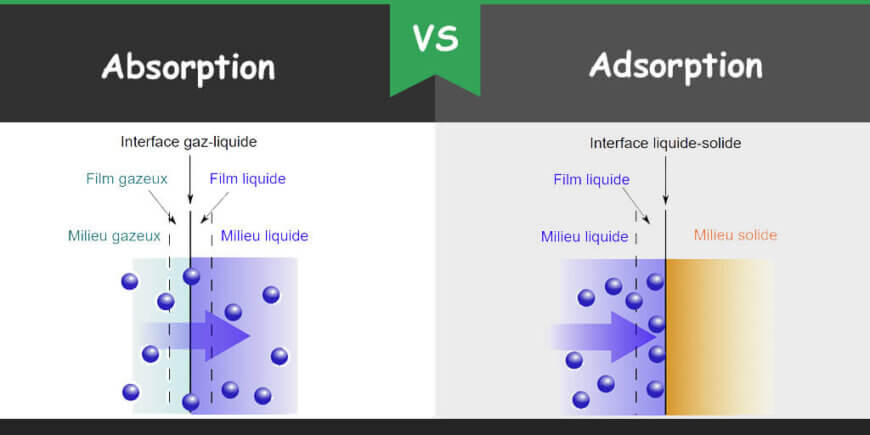
Absorption is the process in which a molecule is dissolved by a liquid or bulk of solid. In the case of bulk solid, solid is called absorbent. Adsorption is a process in which ion, molecule or atom of any substance get attached on the surface of any other substance which is called adsorbent. In absorption, the entire volume of the absorbing substance has involved while in case of adsorption, only the surface of the adsorbing body is involved. Both processes are ubiquitous in everyday life as well as in biological and chemical laboratories.
Contents
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Absorption | Adsorption |
| Phenomena | A bulk phenomena | A surface phenomena |
| Heat exchange | Endothermic process | Exothermic process |
| Temperature | No effect | Influenced by low temperature |
| Rate of Reaction | Occurs at a uniform rate | Gradually increases and reaches an equilibrium point |
| Concentration | Same throughout the body | Different on the surface from the bulk |
| Application/uses | Refrigerant, ice production, cold storage, turbine inlet cooling | Water purification, air conditioning, synthetic resins, chillers, removal of poison from the body |
What is Absorption?
In absorption, the substance or the absorbate (ion, molecule or compound) diffuse completely into other substances or medium which can be liquid, gas or solid. As the absorbate completely diffuses in the other medium so it is a bulk process. The absorbing material or absorbate remains intact with other substance due to the presence of space within the substance but do not show any chemical reaction. When absorbent and absorbate intact with each other through chemical reaction then it cannot be separated easily. Absorption can be of two types; physical adsorption and chemical absorption. In physical absorption, just mass transfer of absorbate into the absorbing medium occurs whereas in chemical absorption, a chemical reaction occurs and an absorbate changes its state.
Applications
The absorption process can be seen everywhere from the absorption of food in the stomach to the industrial applications. Soaking of spilled milk through a paper towel is a common example of absorption. Absorption chillers for space cooling instruments, cold storage, ice production, turbine inlet cooling, etc are all examples of the absorption process. The process of gas absorption by a liquid is used in the carbonation of beverages and hydrogenation of oils.
What is Adsorption?
Adsorption is a surface phenomenon in which a substance is accumulated in solid, gas or liquid form on the surface of another substance which may be in solid or liquid form. The substance which gets accumulated or adsorbed is called adsorbate while the substance on which the adsorbate accumulated is called adsorbent. Alumina gel, silica gel, zeolite, graphite, and activated carbon are some examples of adsorbents. The adsorption process is usually used to separate off a substance through another substance. Adsorbate is loosely held with the absorbent. This interaction can be either physisorption or chemisorption. In physisorption, attachment between the molecules is of weak van der Waal forces. In chemisorption, the interaction between the molecules is through a covalent bond. Desorption is the reverse process of adsorption in which the adsorbed molecules are removed from the surface of the adsorbent.
Applications
Adsorption process has many applications in industries for example adsorption chillers, air conditioning, water purification, and synthetic resin. Adsorption of molecules on the polymer surfaces are used in the development of non-stick coating and in some biomedical devices. In pharmaceutical industries, adsorption is used as a means to enhance neurological exposure of specific drugs. Similarly, activated charcoal is used to treat poisoning of some substances or overdose of drugs. Activated charcoal removes poisons through the adsorption process.
Adsorption and its reverse process desorption are the main principles in chromatography. In chromatography, relative rates of adsorption and desorption on the stationary phase allows the substances to be separated. If the chromatography column favors the adsorption of a substance, the molecule will adhere to the stationary phase and separated from the mixture of chemicals. If the column conditions favor the desorption, the chemicals will be released into the mobile phase of the column.
Key Differences between Absorption and Adsorption
- Absorption is a bulk phenomenon whereas adsorption is a surface phenomenon.
- In absorption, the reaction rate is uniform whereas, in adsorption, the reaction rate is steady and gets equilibrium.
- In absorption, the heat exchange process is endothermic whereas, in adsorption, the heat exchange process is exothermic.
- The absorption process is not affected by temperature whereas the adsorption process is affected by the temperature.
- In adsorption, the concentration of the absorbed substance does not change and remains constant throughout the medium whereas, in absorption, the concentration of the adsorbed substance varies from the bulk to the bottom of the absorbent.
Key Similarities
- Both absorption and adsorption are sorption processes.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, both absorption and adsorption are slightly different from each other and occur in day to day life processes. So understanding their difference is essential.