Respiration is a continuous chemical process which provides energy for the fuel of biological processes such as the growth of cells, muscles contractions, protein synthesis, sending nerve impulses and absorbing molecules for the active transport in the body. Without respiration, the survival of an organism is not possible.
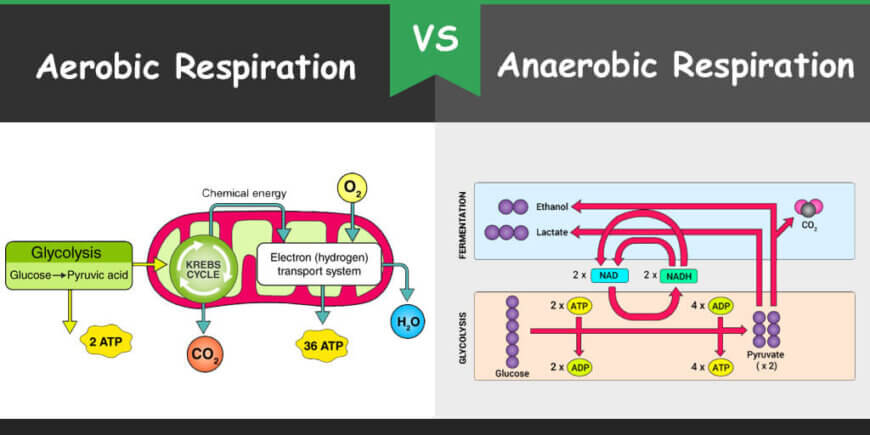
There are two types of respiration; aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration. Aerobic means with “in the presence of oxygen” whereas anaerobic means “without oxygen”. So the process of respiration which needs oxygen for occurrence is called aerobic respiration whereas the respiration which does not need oxygen is called anaerobic respiration. Both aerobic and anaerobic respiration converts the glucose into the energy by using an electron transport chain. But both types of respirations have many differences.
Contents
Comparision Chart
| Basis | Aerobic Respiration | Anaerobic Respiration |
| Definition | Aerobic respiration is defined as the respiration which occurs in the presence of oxygen. | Anaerobic respiration is the respiration which occurs in the absence of oxygen. |
| Chemical Equation | Glucose + oxygen→ carbon dioxide + water+ energy | Glucose→ Ethanol+ Carbon dioxide |
| Amount of Energy | The high amount of energy | Low amount of energy |
| No. of ATP Produced | 38 ATP | 2 ATP |
| Location of Occurrence | Mitochondria and cytoplasm | Only in cytoplasm |
| End Products | Carbon dioxide and water | Carbon dioxide, ethyl alcohol, and energy |
| Stage | Two stages: Glycolysis and Kreb’s cycle | Two stages: Glycolysis and fermentation |
| Function | Energy production | Helps in fermentation |
| Examples | In multicellular organisms such as animals, plants, humans | In unicellular organisms such as bacteria, fungi, yeast, protozoa, etc. |
What is Aerobic Respiration?
In aerobic respiration which is also called cellular respiration, animals break down the food substances for producing energy with the use of oxygen. It occurs in a series of reactions which are catalyzed by the enzymes. The aerobic respiration process occurs in mitochondria of the cells where electrons from the glucose molecules are transferred to the electron acceptor; oxygen. Aerobic respiration starts with the glycolysis which is also called the Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas pathway and also involved the citric acid cycle (Tricarboxylic acid cycle) and electron transport chain. The citric acid cycle is also called the Kreb’s cycle. 40 ATPs are produced in one cycle. Four ATP from glycolysis, two from tricarboxylic acid and thirty-four from electron transport but two ATPs are consumed during glycolysis so net production is 38 ATP molecules.
Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy
While the net amount of energy released is 2900 kJ/mol of glucose. Lactic acid is not produced. The aerobic respiration process goes on always in the plants and animals.
What is Anaerobic Respiration?
Anaerobic respiration is the respiration which does not need oxygen. A small amount of energy is released in cells by the breakdown of food molecules in the absence of oxygen. In animals, anaerobic respiration occurs in muscles during vigorous exercise.
Glucose→ Lactic acid
The lactic acid needs to be converted into carbon dioxide and water by oxidation so it causes oxygen debt that is repaid on the stop of exercise or taking a break of breathing during exercise. Glucose is partially broken down into the energy so a little amount of energy is released during anaerobic respiration. Anaerobic respiration also occurs in some microorganisms and plant cells. It happens in yeasts and called fermentation which is used for wine, yogurt, brewing and bread making. It makes ethanol and carbon dioxide as final products.
Glucose→ Ethanol+ Carbon dioxide
Ethanol is actually the alcohol which is used in drinks while carbon dioxide makes bubbles in the bread during the process and helps the bread to rise.
Key Differences between Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
- Aerobic respiration needs oxygen whereas anaerobic respiration does not need oxygen.
- Glucose break down is complete in aerobic respiration whereas glucose breaks down is not completed in anaerobic respiration.
- In aerobic respiration, a large amount of energy is released whereas, in anaerobic respiration, a small amount of energy is released.
- Aerobic respiration occurs in mitochondria and cytoplasm whereas anaerobic respiration occurs only in the cytoplasm.
- In aerobic respiration, the exchange of gases occurs whereas, in anaerobic respiration, it does not occur.
- In aerobic respiration, carbon dioxide and water are the end products whereas, in anaerobic respiration, lactic acid is the end product in case of animal cells and carbon dioxide and ethanol are the end products in case of plants and yeasts.
- Aerobic respiration is the long process of energy production whereas anaerobic respiration is a fast process.
- Aerobic respiration occurs in a higher level of organisms such as mammals whereas anaerobic respiration occurs in the lower level of organisms such as bacteria, yeast, etc.
Key Similarities
- Both aerobic and anaerobic respiration has a common stage; glycolysis (glucose splitting).
- Both aerobic and anaerobic respiration release energy in the form of Adenosine triphosphate.
- Both aerobic and anaerobic respiration happens in both unicellular and multicellular organisms.
- Both aerobic and anaerobic respiration has one step common in which glucose is converted into pyruvic acid.
Conclusion
It has concluded from the above differences and comparison that aerobic and anaerobic respiration is the biological processes occurring every time in the body of plants, animals, and microorganisms. Aerobic respiration is actually the process of energy production in the presence of oxygen whereas anaerobic respiration is the energy production in the absence of oxygen.