The cells perform millions of biochemical reactions in one full minute for them to replicate for the propagation of life. Cellular functions may seem to have some complexities. Endocytosis is also a complex cellular function that was given by Christain de Duve in 1963. Pinocytosis and phagocytosis are types of endocytosis. Both terms refer to the intake of material through the plasma membrane by forming vesicles, which are membrane-bound droplets located in the cytoplasm of the cell. Endocytosis takes place in the animal cell and very rarely in the plant cell as the plant cell is bounded by the cell wall, which causes interruption in the invagination of the plasma membrane.
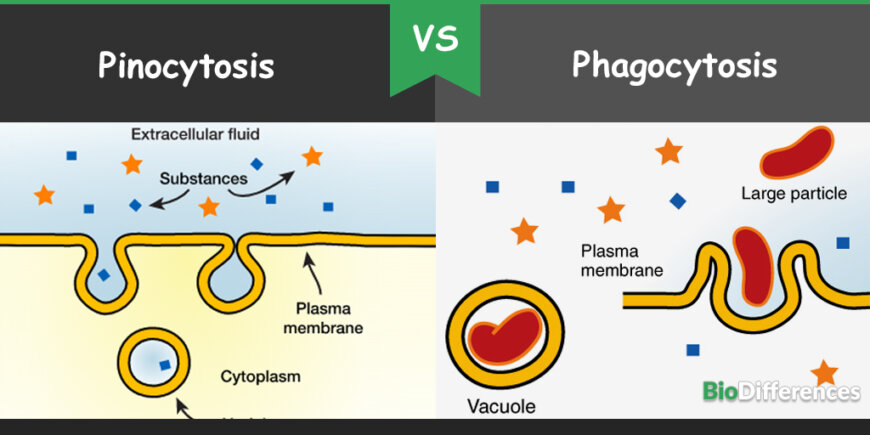
Pinocytosis means cellular drinking, whereas phagocytosis means cellular eating. Pinocytosis and phagocytosis are active processes and require energy as adenosine triphosphate for the uptake of materials. Pinocytosis is an intake of liquid particles with the formation of vesicles called pinosomes, whereas phagocytosis is the intake of solid particles with the formation of vesicles called phagosomes. In both cases, endosomes are developed, which is an invagination of the plasma membrane to develop vesicles. These vesicles find the engulfed particles, which can be solid or liquid.
Exocytosis is the opposite process of endocytosis. In exocytosis, substances are being allowed to move out of the cell by a mechanism that is similar to endocytosis and common in secretary cells.
Contents
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Pinocytosis | Phagocytosis |
| Definition | Pinocytosis is the ingestion of small liquid particles through the plasma membrane, with the help of the formation of vesicles known as pinosomes. | Phagosomes are the process of ingestion of solid particles through the plasma membrane with the aid of lysosomes and phagosomes, which release enzymes to break the larger particles. |
| etymology | The Greek word which means “cellular drinking.” | The Greek word which means “cellular eating.” |
| Method of engulfing | By invagination | By pseudopodia |
| Type of particles for ingestion | Liquid | Solid |
| Substrate specific | Not substrate-specific | Substrate specific |
| Purpose | For the intake of particles | For defensive purpose |
| Vesicles formed | Pinosomes | Phagosomes |
| Role of lysosomes | No role | Lysosomes combine with phagosomes to form a food vacuole |
| Types of particles to intake | Ions, sugar, amino acids, enzymes, hormones | Foreign particles, virus, bacteria, dust, etc |
| Site | In secretary cells, cell linings of blood capillaries | In neutrophils, macrophages, protozoans |
| Examples | Kidney separate nutrients and fluids from the urine to expel from the body by the process of pinocytosis. | Destruction of viruses and bacteria by the white blood cells |
What is Pinocytosis?
Pinocytosis is also called cell drinking. It is the intake of small particles and liquid. Mostly, enzymes, hormones, amino acids, insulin, sugars, lipoproteins are ingested through pinocytosis. Pinocytosis is not substrate-specific and cell takes all kind of surrounding fluids with all solutes present. This process is usually used for taking in extracellular fluids. Cells of the intestinal wall that have microvilli also use pinocytosis for the intake of the nutrients.
Process
In this process, the small liquid particles are attached to the outer layer of the plasma membrane. These small particles are attached to the specific receptors located on the outer layer of the plasma membrane. As a result, the plasma membrane forms the membrane-bounded vesicles called pinosomes, which is an invaginated region surrounding the particles. These pinosomes finally move to the cytoplasm and the engulfed particles are released.
Pinocytosis can be divided into micropinocytosis and micropinocytosis based on the size of the vesicles formed. In micropinocytosis, vesicles formed are of about 1 to 2µm in length whereas in micropinocytosis, vesicles formed are smaller about 0.1µm.
What is Phagocytosis?
Phagocytosis is also called cell eating. This word has derived from the Greek language in which “phago” means “devouring,” and “cyte” means “cell,” and in this process, the particles which are ingested are larger so enzymes are required for digestion. Phagocytosis occurs in single-cell organisms such as amoeba, protozoans and higher animals. In humans, it occurs in white blood cells, such as in neutrophils and macrophages. This cellular process is used for the defensive purpose to engulf foreign particles, harmful viruses, bacteria and other waste materials.
Process
In this process, feet like structures called pseudopodia are formed, which extend to swallow up solid particles to be taken into the cells. Plasma membrane surround and fuses with the particles to be taken into the cells where vesicles are formed, which are called phagosomes. These phagosomes, along with the lysosomes lebirate digestive enzymes, which are helpful in the digestion of the phagosomes. At the end of phagocytosis, the cellular waste that can not be reused is discharged from the cell by the process of exocytosis.
Key Differences
- Pinocytosis is the bulk of intake of fluid matter, including solutes by the cell, whereas phagocytosis is the intake of solid matter by the cell.
- In pinocytosis, the process of engulfing is by the invagination, whereas in phagocytosis, the process of engulfing is by pseudopodia.
- Pinocytosis does not use lysosomes, whereas phagocytosis uses lysosomes along with phagosomes for the digestion of bigger particles.
- In pinocytosis, the substances being ingested can readily be absorbed, whereas, in phagocytosis, the particles are broken down into the simple substances for absorption.
- Pinocytosis is not substrate-specific, whereas phagocytosis is the substrate-specific.
- Pinocytosis is used for the intake of materials, whereas phagocytosis is used for defensive purposes.
- The vesicles formed in pinocytosis is called pinosomes, whereas the vesicles formed in phagocytosis are called phagosomes.
- Pinocytosis is used to intake the enzymes, hormones, amino acids and sugars, whereas phagocytosis is used to engulf dust, foreign particles, harmful bacteria and virus.
- After pinocytosis, exocytosis does not occur, whereas, after phagocytosis, exocytosis transpires at the end.
Key Similarities
- Both pinocytosis and phagocytosis are active processes.
- Vesicles are formed in both processes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, pinocytosis and phagocytosis are biochemical processes of the cell in which particles are ingested for a different purpose. Both differ from each other based on vesicles formed, type of particles engulfed and in some other aspects.