The plasma membrane and cell wall are two important components of the cell. The plasma membrane is present in all types of cells, whereas the cell wall is present only in bacteria, fungi and plant cells. The plasma membrane and cell wall also differ from each other in some other aspects.
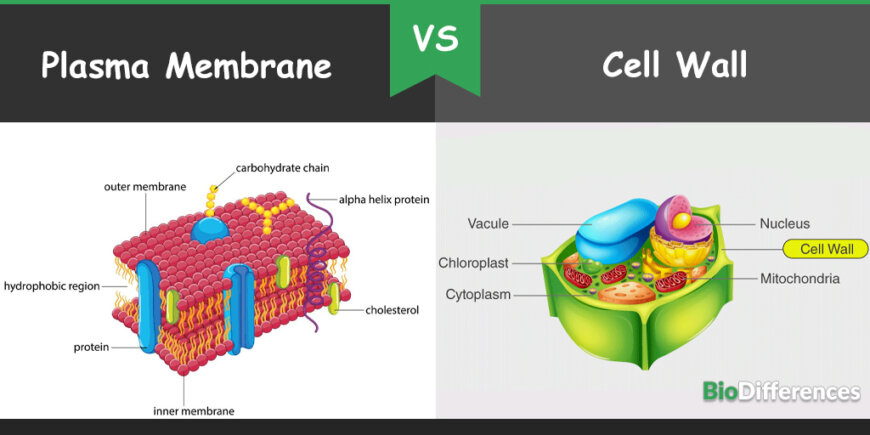
The plasma membrane is composed of a phospholipid layer and its main function is to protect the protoplasm and checks the passage of molecules inside the cell. On the contrary, the cell wall protects the cell from external shocks and provides rigidity and shape to the cell. In the cells in which the cell wall is present, it is the outermost boundary of the cell and the plasma membrane is present beneath the cell wall.
The plasma membrane is a delicate thin layer. It allows the small molecules entry only as it is selectively permeable, whereas the cell wall is the thick and rigid layer and does not allow to pass any molecules.
Contents
Comparison Chart
| Basis for Comparison | Plasma Membrane | Cell Wall |
| Definition | The plasma membrane is the semipermeable membrane composed of phospholipids that surrounds the cytoplasm of a cell. | The cell wall is a rigid layer of polysaccharides lying outside the plasma membrane of the cells of bacteria, fungi and plants. |
| Found | In all type of cells | Bacterial cell, a fungal cell, algae and plant cell |
| Composition | Lipids, proteins and carbohydrates | Cellulose in a plant cell, chitin in fungal cell and peptidoglycan in bacterial cell |
| Thickness | A thin layer, 5 to 10nm | Thick layer, 4 to 20µm |
| Visibility | Visible only through an electron microscope | Visible through the light microscope |
| Permeability | Semi-permeable | Completely permeable |
| Receptors | Present | Absent |
| Metabolic function | Metabolically active and living | Inactive and non-living |
| Nutrition | Need proper nutrition for growth | Does not need proper nutrition |
What is Plasma Membrane?
The plasma membrane is also called the cell membrane of the plasmalemma. It is found in all types of cells and around each organelle of the cell. It is selectively permeable and does not allow all types of material to enter the cell. Hence it is known as semi-permeable as it will enable to pass very selective molecules. This is the reason; it is known to control the traffic of the molecules inside the cell and maintain the internal structure of the cell.
Composition
The Fluid Mosaic Model, which was presented in 1972, is used to describe the structure of the cell membrane. According to this model, the cell membrane has fluid consistency and it moves freely because of its composition Mainly, it is composed of four components; a phospholipid bilayer, proteins (glycoproteins and peripheral membrane proteins), cholesterol and carbohydrates (carbohydrates form glycoproteins and glycolipids in the cell membrane). Proteins pass freely through the cell membrane because of its phospholipid composition.
Functions
The cell membrane performs several important functions for the cell. It is present below the cell wall. If the cell wall is not present, the plasma membrane acts as the outer layer and provides support, integrity and shape to the cell. It is responsible for maintaining the constant internal environment in the cell cytoplasm.
It also provide a vital function in cell signaling and communication. The plasma membrane uses the receptors present on the outer layer of the membrane for the cell to cell communication. These receptors and channels allow specific molecules (ions, nutrients, wastes and metabolic products, etc.) to pass through the organelles and between the cell and the outer environment. The cell membrane also helps in regulating cell growth through the balance of endocytosis and exocytosis.
What is Cell Wall?
The cell wall is present only in a plant cell, fungal ad bacterial cell as the outermost layer of the cell. It is absent in animal cell, so the plasma membrane acts as an outermost layer of the animal cell.
Composition
The composition of the cell wall varies in different organisms. But its main composition is the cellulose, long fibers of carbohydrates including hemicellulose, lignin and pectin. All cell walls contain two layers, the middle lamella and the primary cell wall. But some cells produce an additional layer called a secondary layer. The cell wall of the plants has cellulose as the major component in its composition, the fungal cell wall has chitin and the bacterial cell wall is made up of peptidoglycan.
Functions
The cell wall performs several significant functions. It defends the cell against physical damage and invading pathogens. It also regulates and controls the direction of cell growth. The cell wall also provides the strength, structural support and maintenance of the shape of the cell. It also functions as a storage unit by storing carbohydrates for use in plant growth, especially in seeds. Like cell membranes, it also acts as a selectively permeable membrane by allowing the entry of the small molecules to pass through it.
Key Differences
- The plasma membrane is the phospholipid layer present in all types of cells. In contrast, the cell wall is made up of chitin, cellulose, or peptidoglycan and present only in a plant cell, fungi, or bacteria.
- The plasma membrane is very fragile and is 5 to 10nm thick, whereas the cell wall is very rigid and is of 4 to 20µm.
- The plasma membrane is nonelastic, whereas the cell wall is elastic.
- The plasma membrane is metabolically active and living, whereas the cell wall is metabolically inactive and non-living.
- The plasma membrane needs nutrition to grow, whereas the cell wall does not need nutrition to grow.
- The plasma membrane is semi-permeable and allows selective molecules to pass, whereas the cell wall is completely porous.
- The plasma membrane mainly performs as a check on the entry of the molecules in the cell, whereas the cell wall provides mostly rigidity and protection to the cell.
Key Similarities
- Both the plasma membrane and cell wall give shape to the cell.
- Both provide support and rigidity to the cell.
- Both regulate the incoming and outgoing of the molecules.
- Both protect the cell.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the cell membrane and cell wall perform somewhat the same functions, but they differ from each other in structural composition and presence in different types of cells.